
Docker Containers in AWS — A Complete DevOps Guide
Containers are the backbone of modern DevOps workflows. In this detailed blog we’ll walk through what Docker is, why it matters for DevOps, how Docker runs on AWS, and a practical CI/CD example that ties Docker, AWS, and DevOps together. If you’re training to be an AWS + DevOps engineer, this is the exact practical skillset you’ll repeatedly use.
Why Docker matters for DevOps
- Consistency: A container packages your app + runtime + dependencies into a single immutable artifact. “It works on my laptop” becomes “it works in production.”
- Speed: Containers start far faster than VMs — ideal for CI jobs and autoscaling.
- Portability: Build once, run anywhere (dev machine → staging → AWS).
- Microservices friendly: Small, single-purpose containers map naturally to microservices and modern deployment patterns.
Docker basics — the short version
- Image: A read-only template (built from a Dockerfile) that contains your application and runtime.
- Container: A running instance of an image (isolated process with its own filesystem and network namespace).
- Dockerfile: Text file that defines how an image is built (base image, copy files, run commands, expose ports).
- Registry: A storage service for images (Docker Hub, or AWS ECR for AWS-native workflows).
Example minimal Dockerfile for a Node.js app:
FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY package*.json ./
RUN npm ci --only=production
COPY . .
EXPOSE 3000
CMD ["node", "index.js"]
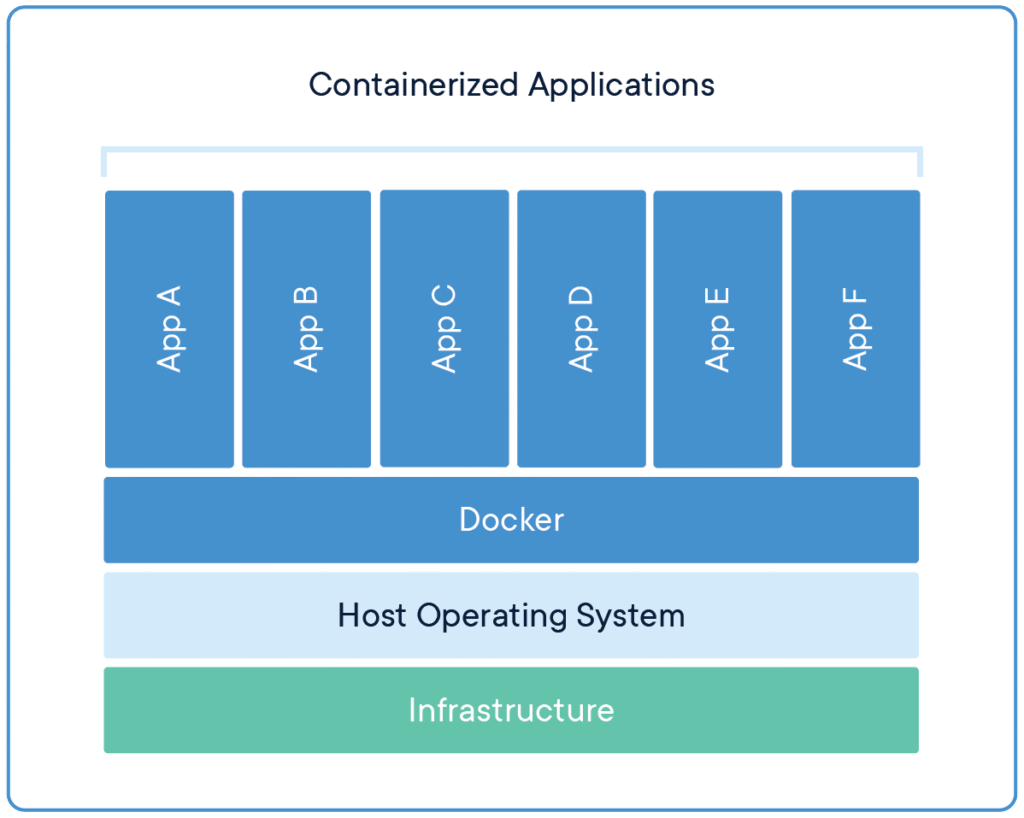
Running Docker in AWS — main options
AWS provides multiple managed ways to run containers. Choose based on control vs. convenience:
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) + Fargate
- Fargate: serverless containers — you don’t manage EC2 instances. Great for simple deployment and cost predictability.
- ECS on EC2: you manage the underlying EC2 instances (good when you need custom kernels or GPU/spot instances).
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Managed Kubernetes. Ideal if you already use Kubernetes or need advanced orchestration (custom controllers, Helm charts).
- AWS App Runner
- Simplified service for web apps and APIs—auto-builds and deploys from source or container.
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- AWS-managed, secure Docker registry where you push your images.
Typical DevOps workflow with Docker + AWS
- Code pushed to Git (GitHub/GitLab/Bitbucket).
- CI pipeline builds Docker image, runs tests, scans image for vulnerabilities.
- Push the image to AWS ECR (tagged with commit or semantic version).
- CD pipeline deploys new image to ECS/EKS/App Runner (rolling update / blue-green).
- Monitor & roll back if metrics/alerts indicate problems.
Example: Build → Push to ECR → Deploy to ECS (Fargate)
Local / CLI steps (high level)
- Create ECR repo:
aws ecr create-repository --repository-name my-app --region us-east-1
- Authenticate Docker to ECR:
aws ecr get-login-password --region us-east-1
| docker login --username AWS --password-stdin <AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com
- Build, tag, push:
docker build -t my-app:latest .
docker tag my-app:latest <AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-app:latest
docker push <AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-app:latest
- Update ECS task definition (can be automated via AWS CLI or SDK) and update service to use the new image.
Automate with GitHub Actions (CI/CD) — simplified workflow:
name: CI-CD to ECS
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v2
with:
aws-region: us-east-1
role-to-assume: arn:aws:iam::${{ secrets.AWS_ACCOUNT_ID }}:role/GitHubActionsDeployRole
role-session-name: gha
- name: Login to ECR
uses: aws-actions/amazon-ecr-login@v1
- name: Build & push Docker image
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
with:
context: .
push: true
tags: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCOUNT_ID }}.dkr.ecr.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/my-app:${{ github.sha }}
- name: Deploy to ECS (update service)
uses: aws-actions/amazon-ecs-deploy-task-definition@v1
with:
service: my-ecs-service
cluster: my-ecs-cluster
task-definition: taskdef.json
This pipeline builds, pushes to ECR, and calls an ECS deploy action. In production you’ll add tests, security scans (e.g., Trivy), image signing, and approvals.
Best practices for Docker in AWS + DevOps
- Small images — prefer slim/alpine base images and multi-stage builds to reduce attack surface and faster pulls.
- Immutable tags — push images with unique tags (commit SHA or semantic version) and avoid
latestin production deploys. - Scan images — integrate vulnerability scanners (Trivy, Clair) into CI.
- Secrets management — don’t bake secrets into images; use AWS Secrets Manager, SSM Parameter Store, or IAM roles (task roles).
- Task/Pod roles — use IAM roles for tasks (ECS Task Role / IRSA for EKS) rather than storing AWS keys inside containers.
- Health checks — configure container and service-level health checks for safe rollbacks and autoscaling.
- Resource limits — set CPU & memory limits so one container can’t starve others.
- CI gating — require tests and security scans to pass before deployment.
Security considerations
- Least-privilege IAM: grant only the permissions a container needs.
- Image provenance: use signed images and approved registries.
- Network segmentation: run internal services in private subnets and use security groups and network policies.
- Runtime hardening: drop unnecessary Linux capabilities, run as non-root where possible.
- Patch base images: rebuild images regularly to pick up security patches.
Observability — logs, metrics, tracing
- Logs: Send container logs to CloudWatch Logs or a centralized logging stack (ELK/Opensearch, Datadog).
- Metrics: Use CloudWatch Container Insights, Prometheus exporters (for EKS), or managed observability services.
- Tracing: Add OpenTelemetry or vendor-specific tracing to trace requests across microservices.
View this post on Instagram
Hands-on mini project (what to build to practice)
Project: Deploy a simple Node.js microservice using Docker → push to ECR → deploy to ECS Fargate with autoscaling.
- Write a small REST API.
- Create a Dockerfile and test locally.
- Create an ECR repo and push the image.
- Create ECS cluster, task definition, and service (Fargate).
- Configure ALB and health checks.
- Set autoscaling rules (scale on CPU or request latency).
- Add CloudWatch alarms and enable logging.
- Automate the pipeline with GitHub Actions including a vulnerability scan step.
This single project covers build, registry, container orchestration, observability, and automation — core DevOps skills.
What you should be able to do after learning Docker + AWS with DevOps
- Build production-grade Docker images and maintain image hygiene.
- Push and manage container images in AWS ECR.
- Deploy and manage containers on ECS (Fargate) and/or EKS.
- Create CI/CD pipelines that build, scan, and deploy containers automatically.
- Secure containers using IAM roles, secrets managers, and image scanning.
- Monitor container health, logs, and performance in production.
Conclusion & Next Step
Docker is the practical entry point to cloud-native DevOps on AWS — it gives you speed, portability, and a repeated, testable delivery model. If you want hands-on, instructor-led training that takes you from Docker basics to building real CI/CD pipelines on AWS, enroll in Sashiraj SmartTech’s AWS with DevOps course — only at $100.
This course covers:
- Docker fundamentals and multi-stage builds
- AWS container services (ECR, ECS, EKS, Fargate)
- CI/CD with GitHub Actions / AWS CodePipeline
- Security, monitoring, and real-world projects you can add to your portfolio
Ready to start? Enroll in Sashiraj SmartTech’s AWS with DevOps course — only $100 — and build the skills employers are hiring for




